The parasitic infection in cats is becoming more concern daily in the USA, UK, European countries, and Australia. Lungworms are parasites found in the lung of cats. Lungworm infection in cats is caused by several roundworm species found in the alveoli and lower respiratory tract.
How Dangerous is Lung Worm in Cats?
Lungworms in cats are one of the most horrible parasitic infections that damage the lung and impair respiration. The infection is life-threatening to cats if you do not seek specific treatment.

Causes of Feline Lungworm Infection
Certain species of nematodes or roundworms are identified that causes infection in the lung of cats. The nematode species that cause infection in dogs are different from cats. The lungworm species of feline are:
- Aelurostrongylus abstrusus or Capilaria aerophila.
- Eucoleus aerophilous.
- Trogostrongylus brevoir.
Transmission or How Cat Gets Lungworm Infection
Feline lungworms are more common in stray cats, and those cats take food from yards or pray. Aelurostrongylus abstrusus enters the cat’s intestine by eating rodents or birds that previously ingested snail-containing parasites. Eucoleus aerophilous infects cats through contaminated feed and water.
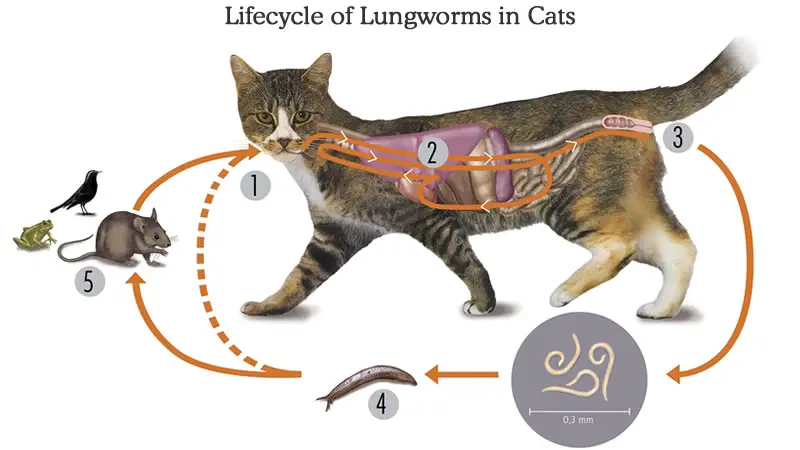
The ingested egg invades the intestinal mucosa and travels through the blood. The egg then reaches the lung and becomes mature, and lays eggs. The eggs traveled to the larynx, and the cat coughed and swallowed the eggs; the eggs passed through the feces and shed in the environment. The eggs in the cat’s feces are ingested by the snails, slugs, rodents, and other small animals that eat cat feces.
Clinical Signs of Lungworm in Cats
Lungworm infection mainly causes respiratory signs. The clinical symptoms depend on the cats’ age, disease condition, and feeding behavior. The most common clinical signs and symptoms are as follows:
- Coughing.
- The breathing rate slightly to severely increased.
- Labored breathing or wheezing.
- Sneezing.
- Respiratory distress.
- In many cases, lungworm infections occur without any visible signs.
- Weight loss.
- Severe cases include emphysema, fluid-filled lungs, and pneumonia.
- Death is seen in kittens but rare in adult cats.
Diagnosis of Feline Lungworm Infection
The diagnosis of lungworm infection is based on the clinical signs, history, and feces examination.
- Clinical history of eating rodents or snails.
- Pathognomonic signs like respiratory distress, coughing, and pneumonia.
- Examination of lungs by auscultation.
- Examination of feces for parasitic eggs.
- Radiographic examination (X-ray) of the lungs.
- Complete blood count.
- Tracheal wash examination.
- Bronchoscopy.
Treatment of Lungworm in Cats
The lungworm infection is challenging to treat and needs continuous anthelmintic administration for two months. The effective anthelmintics are:
- Albendazole.
- Fenbendazole.
- Praziquantel.
- Levamisole.
- Ivermectin.
If the condition is severe and damage to the lungs occurs, the cats need to treat with antibiotics and corticosteroids.
Prevention of Feline Lungworm Infection
The infection is more in stray or outdoor hunting cats and less common in inhouse cats. The parasitic disease in cats can be prevented by taking the following measures:
- Discourage cats from hunting rodents or snails.
- Cleaning of the garden from cat feces.
- Treat your cat with appropriate preventive anthelmintics.
Final Talk on Lungworm in Cats
Lungworm in feline species is common and, if left unnoticed, becomes severe. The condition is worst in kittens. The parasite occurs in the lungs, multiplies there, and causes severe damage to the cat’s lung. You can prevent the parasitic infection in your lovely cat by taking a few simple preventive measures. In my article, I have discussed most of the points briefly. I think this information will help you a lot.