To know the horse health condition is critical as a horse owner. This article I shall provide some necessary horse information for control and manage the horse Health. As a horse lover, most of the cases you will face some problems which basic pieces of information you will need for horse health. In most of the article, I found scattered information. In my discussion, you will get some necessary information in concise form.
15 Basic Horse Health Issues for You
Maintain a good Horse Health to learn about the anatomy of horse, horse behavior, breeding, proper care of hoof, skin problems, eye problems, first aid of horse, colic, lameness and some most common horse diseases, vaccination and worm control measures of the horse, horse diet and feeding behavior, and more. This article helps to know the essential pieces of information related to the horse health.
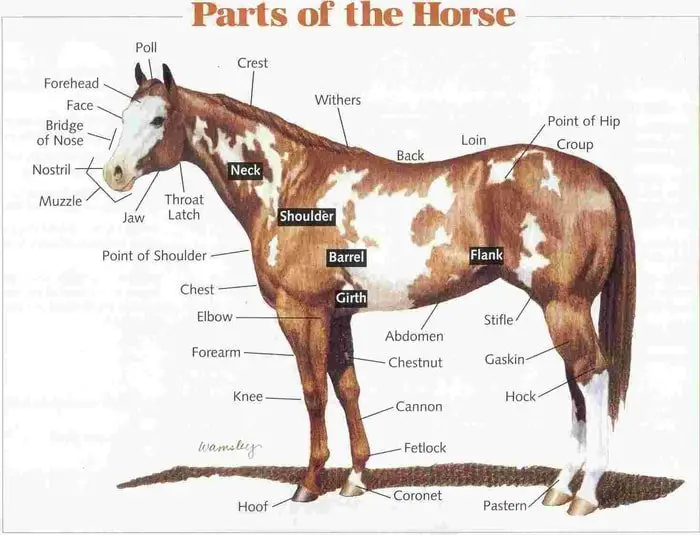
1. Horse Anatomy
It is crucial for the horse owner to be familiar with the anatomy and points of the horse. This will allow you to converse with veterinary surgeons and other owners about problems your horse has, and to recognize what structure may be involved in injuries or wounds. It is vital that you know what you know is standard so you can identify abnormalities. You should be familiar with the shape and form of your horse. One of the basic anatomical information is Horse Digestive System.
2. The Housing of Horse
Correct location of fences, lanes, buildings, and stockyards on a horse farm is essential for efficient operation and management. A well-planned property will save money through reduced labor and running costs. It will also be a more valuable piece of real estate. Horses are useful animals and must be protected at all times. The ideal location for farm buildings is in the center of the property. The materials allow easy access to all parts of the property. When deciding on a site, consider such factors as stock and vehicle access, drainage, and wind protection. You will also have to find the cost of providing the place with electricity, telephone lines, and water supply. Choose a site that has the best combination all these factors.

3. Horse Behaviour
Knowledge of horse behavior patterns is essential for any person dealing with the horse. Knowing how a horse can be expected to react under certain circumstances may often make the difference between success and failure when educating or competing on the horse. It may also make the difference between safe handling and potential injury to either the horse or the rider.

4. Horse Breeding
Reproductive efficiency of an equine breeding operation is a cooperative effort between the Horse Health and the attending veterinarian. The objective is to produce the maximum number of healthy foals, at the least expense, year after year. The means by which this can be achieved are the essential factor of a broodmare operation.
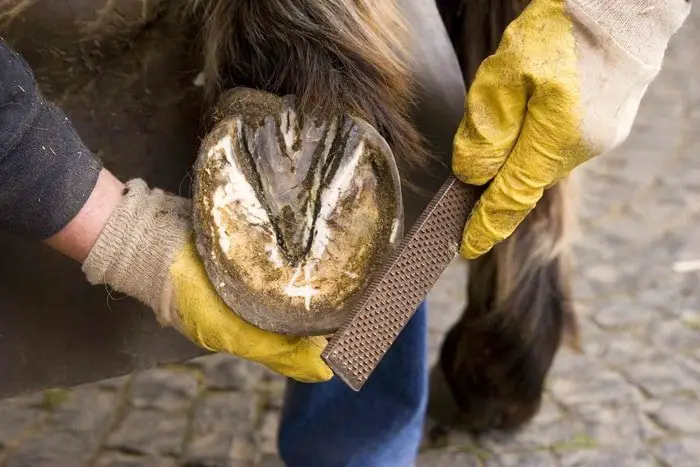
 5. Horse Hoof Care
5. Horse Hoof Care
“No foot, no horse,” is an old phrase that can be taken literally because a lame horse cannot be used. If the legs and feet are no good, then the horse is virtually useless. So hoof care is critical to Horse Health. The detail information of horse hoof structure, horse hoof trimming and horse hoof diseases you will know detail in my articles.

6. Horse Diet
The nutrition value of the horse feeds and horse feed supplements:
- The feed requirements of horse Health vary depending on age and stage of growth, exercise requirements and maternal status.
- Horses must be fed to maintain body condition. When pasture cannot preserve a horses condition, a supplement must be supplied.
- Horse owners are offered many nutritional supplements that are purported to make their horses run faster, jump higher, reproduce more readily and grow better feet and hair.
- Supplements may be used to provide energy, protein, minerals, and vitamins that might be deficient in the basic ration.
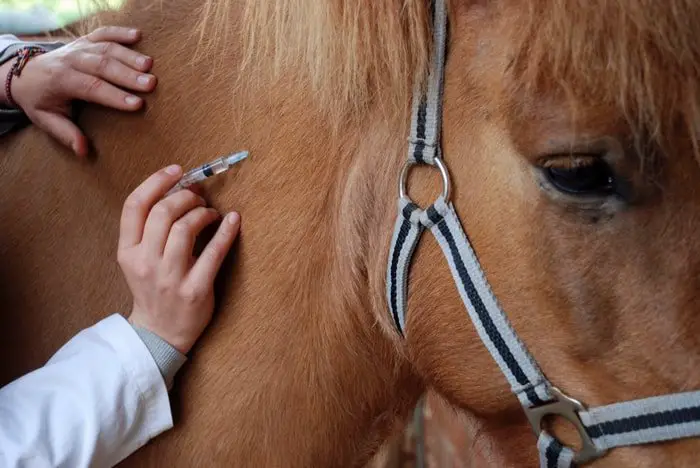
7. Horse Vaccination
There are more than a dozen bacterial and viral diseases of Horse Health for which vaccines are presently available. Vaccination is a useful preventive measure against some infectious diseases. Two dominant horses vaccines are available- one immunization against tetanus, one against strangles. A vaccine against Salmonellosis is also used on some studs.

8. Worms and Worm Control of Horse
The major worms which affect horses in Australia are the large and small strongyles, and roundworms. Stomach bots do not cause a significant problem for most horses. The typical signs of worm infestation are tail rubbing, pale gums, ill thirst, colic, and poor coats. Worms can also cause diarrhea or sudden death.
The most common worms which affect the Horse health are Large strongyles, Small Strongyles, Roundworms, Pinworms, Tapeworms, Threadworms, Lungworms, and Bots.
9. Worm Control, Treatment, and Prevention of Horse
An effective worm control program will be of substantial benefit to your horses, particularly foals and growing horses. It will reduce the incidence of disease and correspondingly lower your veterinary bills. It could also reduce your horses look better.

10. Prevention of Horse Worm
The simple work plan for prevention of worms in your horse is:
- Collect drippings every day, if possible, and at least twice a week.
- They are giving the young horse the cleanest paddocks.
- You use feed bins and hay racks rather than feeding on the ground.
- Harrow paddocks in the hot, dry months (summer in southern Australia, winter in northern Australia) to break up droppings and kill worm larvae.
- Harrow a paddocks if you are going to spell a paddock during hot, dry months or colder winter months.
- Rotate horses to fresh pastures or pastures grazed by cattle or sheep.
- Remove bot eggs from the hair on legs and body in autumn.
- Do not overstock horse paddocks.
- You may rotationally graze or mix grazing with cattle or sheep.
11. Worm Treatment of Horse
Use an effective product. Check for resistance after worming with Warmest 10-14 days after inching. Calculate the correct dose. Weigh the horse or use Caprice Horse, the weight Estimator. You ensure that the entire dose is administered. Rotate wormers every 12 months- use wormers from one chemical group for the next 12 months. You treat foals from 6-10 weeks of age and handle mare just after foaling. For more specific advice and a detailed control program for your property contact your veterinarian.
12. Horse Skin Diseases
There are different types of common skin diseases of Horse Health. To help you work out what may be wrong with your horse’s skin. Horses with rain scald, for example, may show both”hair loss” and “weeping sores with scabs.” As the appearance of these diseases can vary greatly, especially after treatments have been given, you should consult your veterinarian wherever necessary. The standard skin diseases of horse Health are:
- Bacterial acne
- Bee stings
- Big Leg
- Buffalo fly bites
- Ear Mites
- Fibroma
- Lice

- Fly worry
- Leg mange
- Melanoma
- Mosquito bites
- Nodular necrobiosis
- Urticaria
- Warts
- Ticks
- Sarcoid
- Tail itch
- Rain Scald
- Ringworm
13. Horse Wound Management
Skin wounds are a significant problem for owners of all horses that kept in the paddocks. Despite the best facilities, such as post-and-rail fencing or electric fencing, horses still manage to get themselves tangled up and cause wounds. Some horses are kept enclosed by fences made of barbed wire, ring lock or loose plain wire, that provide a significant risk of injury. Horses can also suffer injuries during the competition that damage the skin and the deeper structures.
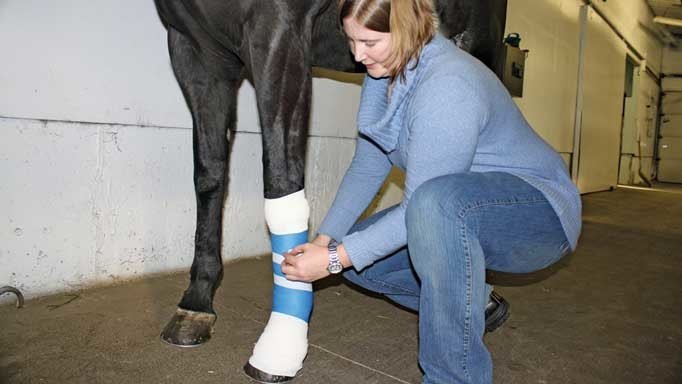 The major problem is that separated horses skin edges heal very slowly and so there can be long periods of recuperation after seemingly minor wounds. Many wounds are not amenable to stitching, and this can lead to a repair process that lasts for months and leaves large scars.
The major problem is that separated horses skin edges heal very slowly and so there can be long periods of recuperation after seemingly minor wounds. Many wounds are not amenable to stitching, and this can lead to a repair process that lasts for months and leaves large scars.
The outcome of a wound depends on many factors:
- The site of the wound-head wounds heals far quicker than leg wounds, for example, while hock wounds are terrible news.
- The type of the wounds-abrasions, contusion, laceration, puncture.
- The size of the wound
- The extent of damage to deeper structures including muscle, tendons, joints, bone, blood supply, nerves.
- The orientation of the wound-vertical wounds heals more quickly than horizontal injuries.
- Whether or not it is infection-this is particularly essential when deeper structures such as joints or bone damaged in a wound.
14. Horse Wound Suturing
If a wound can be sutured and the sutures stay in place, then the healing process will be relatively rapid, between 14 and 28 days. However, many injuries cannot be sutured because of the following reasons
- Delay between the injury and suturing of more than 4-6 hours
- Disruption of blood supply to the lower edge of the wound resulting in the lower flap dying back and the sutures pulling out.
- Excessive swelling around the wound
- Contamination of the injury leading to infection.

Wounds in areas with a better blood supply, fewer movements and less swelling, such as the head or the body, will heal far more quickly and easily when sutured than wounds on the legs. Most leg wounds are not able to be sutured successfully unless they are seen very early after the injury.
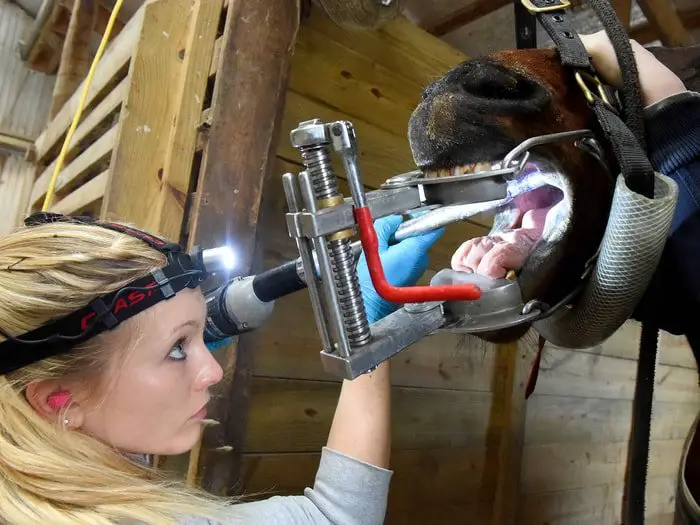
15. Dental Care of Horse
Dental care of Horses is crucial factors for Horse Health. The teeth of a horse should be examined at least once every 12 months if it is grazing. Horses which are stabled or fed concentrates should have their teeth checked every six months. Young horses will need more frequent inspections. The sign of dental diseases of Horse Health is: Rate of chewing, Quidding, Bolting of food, Unresponsiveness to the bit or head tossing, Excessive salivation, etc. There are different types of tooth problems. They are Sharp cheek teeth, Shear mouth, Wave mouth, Step mouth, Smooth mouth, Imperfect meeting of teeth, and an abnormal number of teeth. This type of dental problems is treated with oral medication, injection, and vaccination. Many therapeutic products must be administered orally to horses. They may be applied:
- As a paste.
- Mixed in the feed.
- Via a stomach tube.
- Via a syringe after being dissolved in a solution.

Assessment of The Sick Horse
You can make a better assessment of the severity or cause of the problems your horse as if you can make an essential clinical examination of a sick horse. The findings of a clinical exam can be discussed with your veterinarian and can be used to help determine the need for a visit. To appreciate changes, you need to know what is normal for your horse, so you should examine it when it is problem-free to be ready for the day when problems do occur. There are many factors to consider:
- Body temperature
- Heart rate
- Hydration status
- Mucous membrane color
- Emergency destruction
First Aid of Horse
First aid of horse refers to steps which can be taken to improve a condition, or at least prevent it from worsening before a vet arrives. While most serious states require veterinary attention, as long as the owner is sensible and institutes correct first aid, there are only a few true emergencies that require immediate veterinary care.
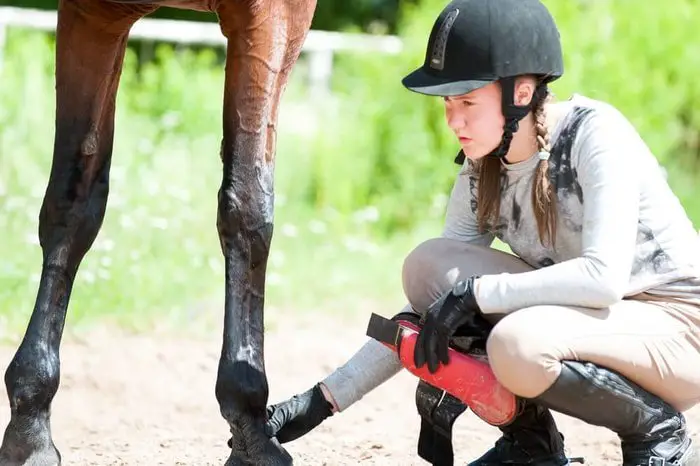

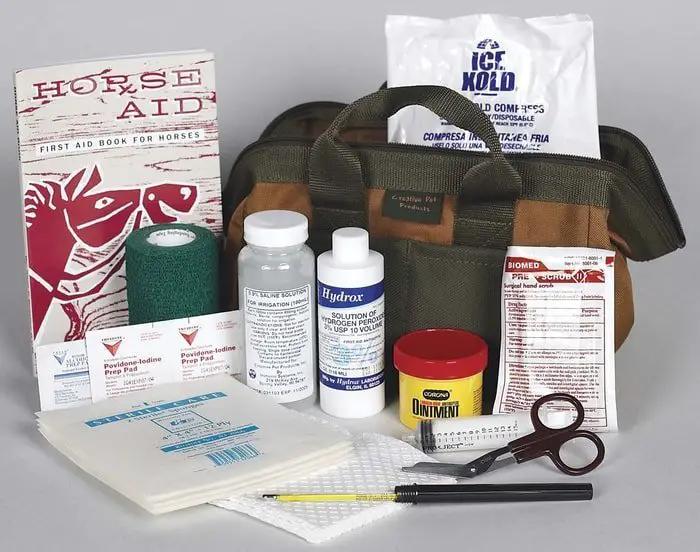
First Aid Kit for Horse
The following items should be kept together as a kitTwo rolls 75 mm Elastoplast
- Two turns 75 mm elastic bandage
- Twitch
- 1 roll of cotton wool
- 1 packet of gauze swabs
- A disinfectant solution, for example, Betadine
- Antibiotic powder
- Blunt-ended scissors
- Tetanus antitoxin
When You Call the Vet
It is essential to know when you call the vet. While most serious conditions require veterinary attention. The vet expert prevented the critical state and handled the dangerous situation. Sometimes you need to help a veterinarian to take care of your horse and maintain your Horse Health.
The Concluding Remarks
There is a lot of information you should know how to maintain horse health as a horse owner. In one article, it is not possible to accumulate all necessary health information. In my above article, I have tried my best to highlight the basic horse health-related issues in very briefly. For more information, you need to detail study the links and reference papers. However, the more to taking care of your horse you need to know in details. There is no short-cut to your experience.
If you are benefited by the above writings, please share with your friends through social media.