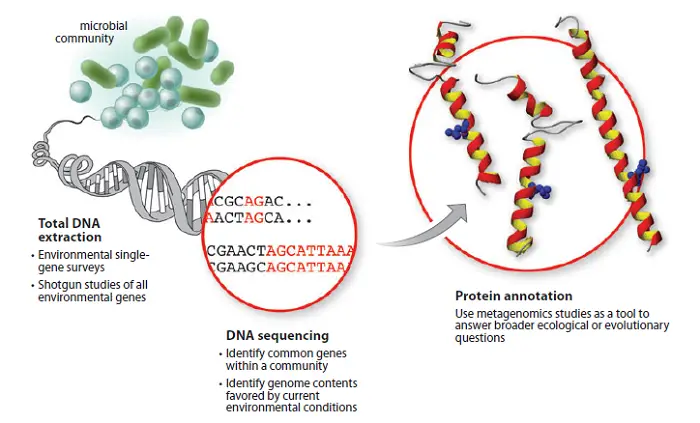
Metagenomics is a field of study that involves the analysis of genetic material recovered directly from environmental samples. Unlike traditional genomics, which focuses on the genomes of individual organisms, metagenomics examines the collective genetic material of entire communities of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, viruses, fungi, and other microbes.
Key Aspects of Metagenomics
Here’s an overview of metagenomics and its key aspects:
- Sample Collection: Metagenomic studies begin with collecting environmental samples from various habitats such as soil, water, air, and the human body (e.g., gut microbiome, skin microbiome).
- DNA Extraction: Genetic material (DNA or RNA) is extracted from the collected samples. This DNA represents the genomes of all microorganisms present in the environment.
- Sequencing: The extracted DNA is sequenced using high-throughput DNA sequencing technologies, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS). This generates vast sequence data representing the genetic diversity within the sampled microbial communities.
- Bioinformatic Analysis: Computational tools and algorithms analyze the metagenomic sequencing data. This includes tasks such as assembling short DNA sequences into longer contiguous sequences (contigs), taxonomic classification of sequences to identify the organisms present, functional annotation to determine the genes and metabolic pathways encoded in the genomes, and comparative analysis to understand the ecological roles and interactions of different microbial taxa.
Applications of Metagenomics
- Microbial Diversity and Ecology: Metagenomics enables researchers to study the diversity and distribution of microbial communities in various environments. It provides insights into microbial ecosystems’ composition, structure, and dynamics and their responses to environmental changes.
- Bioprospecting and Natural Product Discovery: Metagenomics allows for discovering novel genes and enzymes with potential biotechnological applications, such as biofuel production, bioremediation of pollutants, and the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and industrial chemicals.
- Human Microbiome Research: Metagenomics is used to characterize the microbial communities in the human body (e.g., gut microbiome, skin microbiome). It helps understand the roles of these microbial loads in human health and disease, including their contributions to digestion, metabolism, immune function, and susceptibility to various disorders.
- Environmental Monitoring and Biomonitoring: Metagenomics can be employed to assess the impact of environmental disturbances (e.g., pollution, climate change) on microbial communities and ecosystem health. It is a valuable tool for monitoring environmental quality and identifying indicator species, or biomarkers, of ecosystem health.
- Food Safety and Quality Control: Metagenomics can be applied to surveillance food-borne pathogens and spoilage microorganisms in food production environments. It aids in ensuring food safety and quality control and developing strategies for microbial risk assessment and management.
Metagenomics provides a holistic view of microbial communities and their genetic potential. It offers numerous opportunities for scientific discovery and practical applications across various fields, including ecology, biotechnology, medicine, and environmental science.