Foot and hoof of the horse is the most important part of a horse. The relation between the horse and its foot is just like the relationship between vehicle and wheel. There is a proverb that, a horse without foot has no value. A strong, healthy foot is essential for the horse. Various types of diseases are seen on horse foot. If these are not treated in time, the foot can be damaged permanently. So, It is very essential to diagnose horse hoof diseases carefully and treat them properly.

Horse Hoof Diseases
As a horse caregiver, you must regularly check the soundness, health, damage and any injuries of the horse hoof. There is a proverb that “ no hoof, no horse.” You must be enough knowledge about the anatomy of the horse foot and hoof to ensure the proper care and management of horse hoof diseases and keep your horse fit for its purpose.
The common horse hoof diseases are laminitis, thrush, ringbone, keratoma, corn, and sole bruises, crack of the hoof wall, navicular disease, quittor, abscess in the hoof, white line disease, thin sole, hygroma, keratocele, cidito, picked up Neil, sheared heels and quarters.
Signs Of Healthy Horse Hoof
As a horse caregiver, you must check the health status of the hoof every day in the morning before taking him out of the stable for works. There are some common signs of the unhealthy hoof of a horse that reminds you of the horse hoof diseases.
The common signs of horse hoof diseases are sudden onset of lameness, hot or painful hoof, foul-smelling of black discharge from hooves, elevated body temperature, and pulse, shifting weight off of a leg, some cracks or holes may be noticed in the hoof wall, giving resting, pointing or standing on a leg, swelling, and bruises near the base of the hoof, brittle of hoof wall.
If you noticed any of the above signs in your horse or its hoof, you must immediately contact your vet and take the necessary care of the horse hoof. In this article, you will get an overview of Horse Hoof Diseases in a nutshell.
1. Horse Hoof Diseases: Abscess
After an injury to the horse hoof may be contaminated by the secondary bacterial infection which leads to the formation of an abscess. An abscess is one of the most common horse hoof diseases which appear all over the world. The condition is manifested by the presence of swelling in the hoof, pus, or blood come out from the sole and generally hot in the area. The horse showing lameness and a painful gait.

The simple treatment of an abscess is the drain out of pus from the hoof and dressed with tincture iodine. Your vet may give some antibiotics if the condition is severe and rest for a few days.
2. Canker
When hypertrophy is seen in horn-producing tissue for long days; then it is termed as Canker. This disease can be seen in one or both legs. Usually, the hind leg is much prone to this disease. This disease is seen in drought horses. The causes of Canker are the standing on the damp floor or urinated floor and lack of pressure on the frog of the horse hoof.
Recommended Post: Most Easy Methods of Identification of Horses
The disease is manifested by the horn tissue remains wet and soft after suffering from the disease, after that, horn tissue of sole gets attacked, and white pus may be produced in case of microbial attack. To manage the canker in horses, you must clean the affected area with clean water and apply some antiseptics on the hoof. The stable must be thoroughly clean and dry regularly. The bandage should be changed regularly, an antibiotic may be given with the advice of your vet.
3. Laminitis
Laminitis is one of the most common horse hoof diseases which is characterized by the inflammation of the sensitive laminae of the horse hooves. The disease is characterized by the lameness and oozing of pus or fluid from the joint of the hoof wall with the coronary band.

The laminitis is caused by the poor trimming of horse foot, feeding excessive amounts of grain, medication with steroids, injury, and toxins from colic. Acute laminitis is an emergency and needs immediate veterinary and farrier care.
4. Corn and Sole Bruises
When the sensitive laminae (example: sole, bar, and bar angle) is harmed, then it is called corn. Most of the time, the sensitive laminae of the sole area is injured. In the case of a braced sole, one part of it is injured by some stone or horny structure during walking or riding.
The cause of the corn and some bruises in the insufficient trimming of the foot, improper balance of weight in the frog, excessive erosion and hit on the coronet, and over racing. The disease is manifested by frequent lameness, pain sensation in the affected area, and elevated body temperature.

The condition could be easily managed by removal of shoe and null from the horse foot, removal of tissues from the sole, make wet the hoof if it was too dry. You can use bar shoes to remove the pain and after the removal of pus and dead tissues wash with antiseptic solutions.
5. The crack of Hoof Wall
When there is a crack in the wall of a hoof, is termed as Sand crack. This crack can be seen on the whole wall starting from the coronary band. This disease is seen in a quarter of the foreleg and the region of the hind leg.
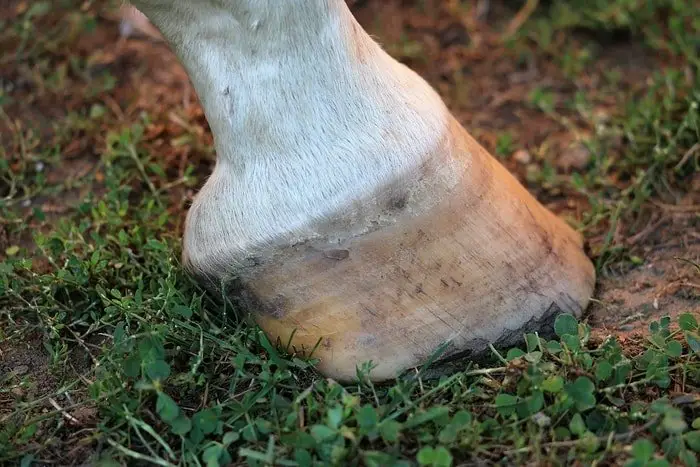

The causes of the crack are the excessive growth of horn tissues, hit on the coronary band, and drying or thinning out of the hoof wall. The symptoms of the disease are the cracking of the hoof wall and in case of any infection pus or blood may come out through the crack.
The treatment of the crack is the surgical removal of the extra tissues and the application of vaseline in the affected hoof. If pus or blood comes out dressing with antiseptics and antibiotic treatment may be given by the vet.
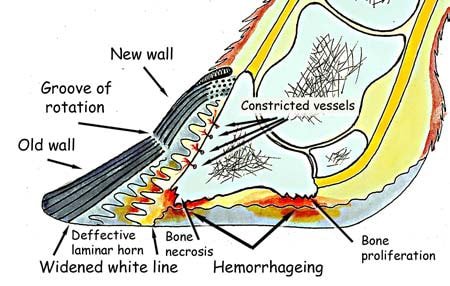
6. Navicular Disease
The condition is called any type of heel pain is maybe called navicular disease and is characterized by lameness and painful gait of the horse. The cause of the disease is genetic, improper nutrition, continuous exposure to unusual ground like hard, rocky surfaces, and working in a too tight or small circle.
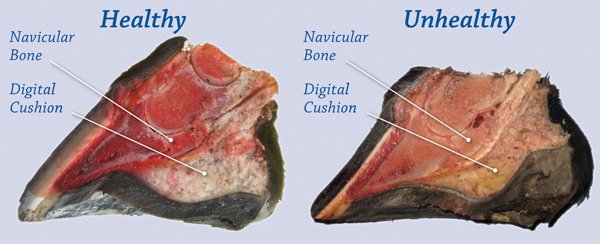
Removal of the cause is the main treatment of the navicular disease, a supply of balanced ration, use proper shoe during working on a hard surface, and take necessary advice from your veterinarian.
7. Horse Hoof Diseases: Quittor
Quitter is the old rotten disease of collateral cartilage of the third phalanx of a horse hoof. The disease is characterized by pus formation in the site of cartilage, necrosis, and coronary band. This disease is usually seen in the front leg of the horse.
The main cause of this disease is a direct hit on lateral cartilage, porous infection in this site may cause this disease, and his disease may spread by corn disease. The clinical symptoms of the disease are swelling of the affected cartilage, and the affected parts may spread up to the coronary band. The area becomes sensitive, and pus may come out through one pour more sinus tract. These may cause severe complications by spreading the disease in other parts.
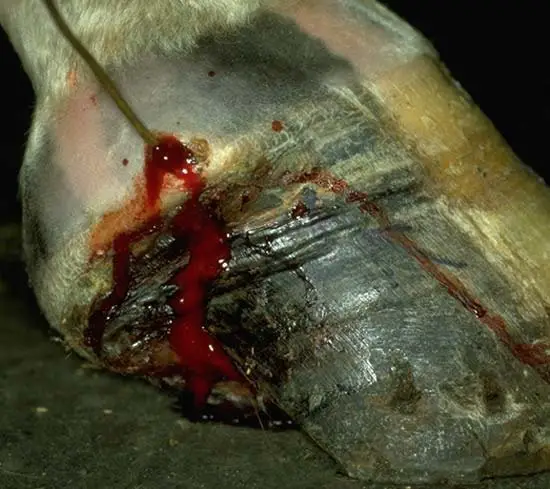
The management of quittor is affected tissue will be cleaned properly, and the sinus tract should be cleaned with mild antiseptic solutions. A protective bandage may be applied to the affected parts and antibiotics may be given in serious cases by the consultation with the vet. Anti-tetanus serum may be given to the affected horse.
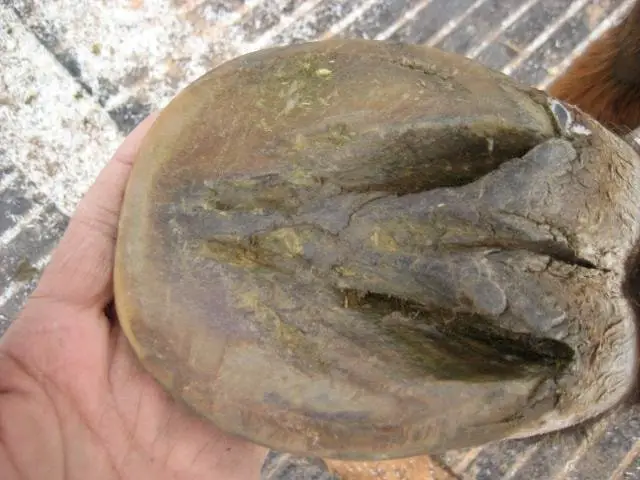
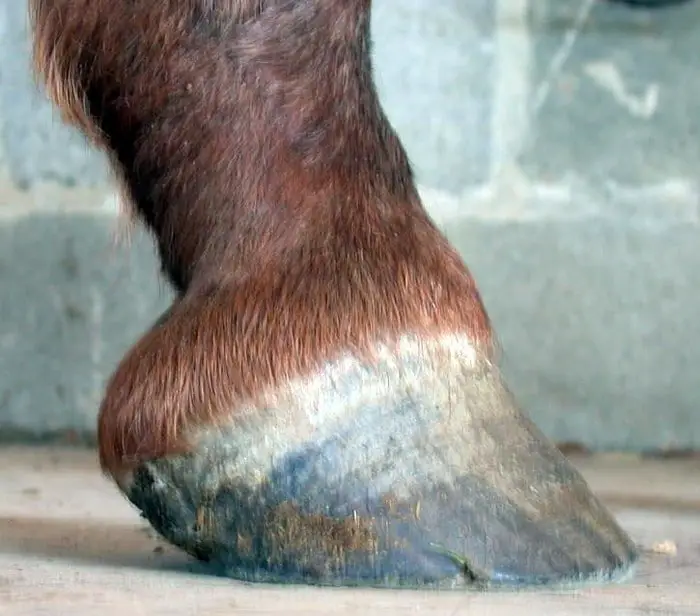
8. White Line Disease
If you noticed any difference in the hoof white line then immediately contact your farrier or vet about the white Line disease. Some bacteria or fungi may infect the injured white line, and the situation causes more serious. You should immediately contact your vet and farrier to remove the dead tissues from the white line, drain out pus, and dressing with antiseptics is the treatment.
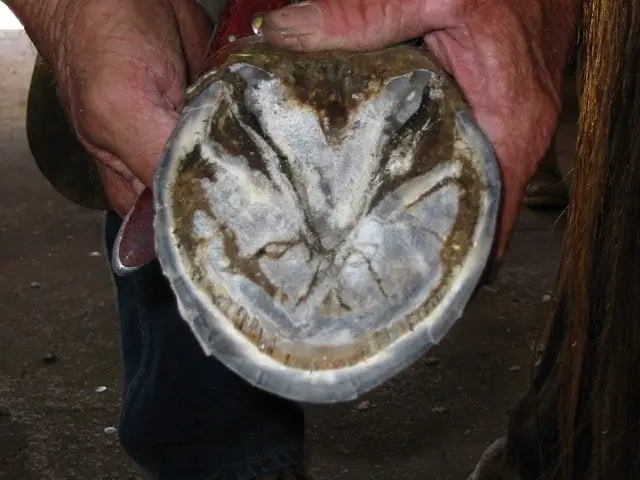

9. Horse Hoof Diseases: Thrush
The degeneration of frog tissues of the horse hoof is called thrush, and the horse hoof disease is characterized by the black discoloration of the hoof sole and the presence of dead tissues. The condition thrush is developed in the sole due to the long time standing of the horse on the wet floor and lack of pressure on the frog of the horse that leads to necrosis of tissues.
The thrush is manifested by the oozing of bad pus from the frog and infected sulci of the frog, elevated body temperature, and lameness of the horse. The care and treatment of thrush are cleaning of affected tissues and removal of dead tissues. The hoof should be clean with 10% formalin, and you must keep your horse in a clean and dry place. The vet may apply antibiotics based on the severity of the disease.

10. Ring Bone
The condition of horse foot when the excessive accumulation of horn tissues in the first, second, and third phalanx of the digit of the horse is known as ringbone. The disease is seen as the pastern or coffin ankylosis in the horse. The cause of the disease is mostly genetic, and other associated causes are insufficient Calcium or Phosphorus in the ration and continuous injuries in the periosteum of the digits.
The disease is characterized by the presence of a new bony structure around the pastern or coffin joint, lameness in case of trotting and the condition will be aggravated if you are not giving proper care at the right time.
The condition of the ringbone could be managed easily in the early stage by applying a cold bandage to the affected joint. You can check the ratio of Ca and P and supply one spoon of extra bone meal in the ration. The horse should be given adequate rest up to recovery.
11. Sheared Heels and Quarters
There are two bulbs on the hoof of a horse. Both bulbs contact simultaneously on the ground when the horse walks or stands. The bulb of the heel touches the ground first and the horse becomes imbalance to bear the weight of the body. The condition leads to the upward displacement of hell which leads to the lameness and painful condition of the hoof.

The lameness may lead to navicular disease, injuries to the hoof wall, and thrush. The fault is hoof trimming, and fault in the hoof conformation may often lead to sheared heels in the horse.
12. Thin Sole
You may find some have thin soles due to lack of care or naturally. The sole protects the coffin bone, and the thin sole may lead to thrush or damage of coffin bone or bruises. You can use a gel between the shoe and sole to protect the thinly soled hoof. Regular care of horse hoof with experienced farrier will reduce the problems of this sole.
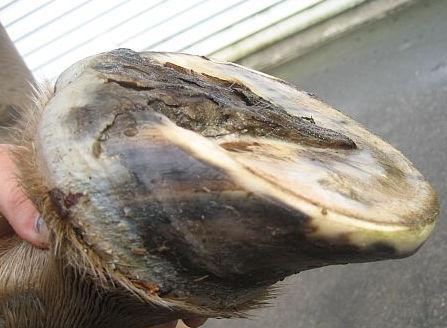
13. Horse Hoof Diseases: Keratoma
Keratoma is the condition in which corn tumors developed in the inner side of the hoof wall. The size of the tumor can be from 1 inch to 3 inches. This disease can be seen in some parts of the wall or the whole area. This tumor looks like a pyramid, conical, or irregular in shape. The causes of the disease are regular irritation in the sensitive laminae of the coronary band and excessive hits on the soft tissues.

In Keratoma lameness may or may not be present but septic juice may come out from the infected sensitive laminae. Removal of the tumor is the main treatment if lameness may not be present. You may give ATS or TT and antibiotics in severe cases.
14. Picked Up Nail
When a sensitive part of the laminae is pressured by any external matter ( shoe nail), then it is called the Picked up nail. When any pin pierces the sensitive laminae, it is called nail bind which becomes very harmful for the horse if the depth of infection reaches up to the frog.
Recommended Post: 15 Most Popular Race Horse Breeds You Must Know As A Horse Racer
The main causes of Picked up are the entrance of part of a nail in the sensitive laminae during the null fitting and any external pressure on the laminae during movement. A picked-up nail is characterized by lameness and after removing a nail, the lameness is finished.
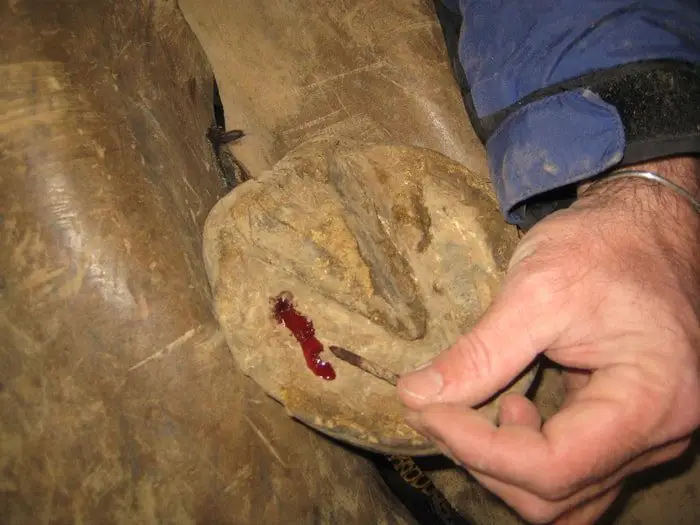

There is no specific treatment of picked-up nail, removal of the nail is the main treatment. If any pus is present, dressing with tincture iodine and remove pus and dead tissues. In a severe case, your vet may suggest antibiotics and ATS or Tetanus Toxoid.
15. Hygroma
Old inflammation of the bursa of the knee joint is called hygroma which is characterized by subcutaneous inflammation. This disease is seen in the elbow region of the horse and is most common in racing horses. The main cause of the hygroma is the continuous hit on the bursa and infection in the elbow region may lead the disease more aggravated.
The hygroma showing by the thickness of the tissues in the bursa and its surroundings, accumulation of fluid in the elbow region, the edema may rupture if the infection is present in the area. There is an absence of lameness in the horse affected with hygroma.
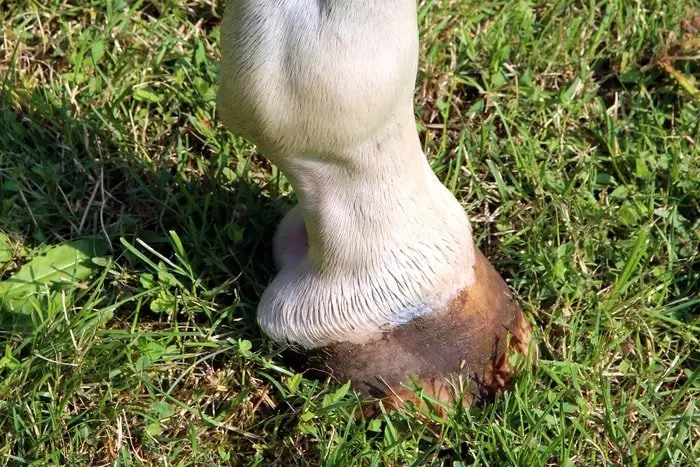

Removal of the causes of irritation is the main treatment of hygroma. You can give heavy bedding in the stall, and adequate rest to your horse, and apply cold therapy by ice in the affected region will help to reduce the edema.
In Conclusion on Horse Hoof Diseases
A few special diseases amongst the horse hoof diseases which occur frequently, I have discussed according to the importance. In fact, treatment of foot disease is very difficult. Practical experience is required to cure horse hoof diseases. The treatment of horses should be avoided with little knowledge. So, it is very essential to have sufficient knowledge about horse hoof before its treatment.
Most horse hoof diseases can be removed at the early stage of disease if you are attentive and take adequate care regularly. As a horse caregiver, you must maintain regular contact with your vet and farrier and check by them at a constant interval. If the above information helps you, please subscribe to our website and share it via social media.