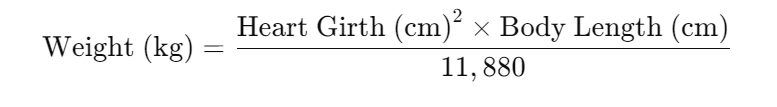Horse weight refers to the body mass of the horse, typically measured in kilograms or pounds. Calculating horse weight encompasses the entire body of the horse, including bones, muscles, organs, fat, and fluids. Understanding a horse’s weight is essential for several reasons, including health management, nutrition, medication administration, and overall well-being.
Significance of Horse Weight
The significance of horse weight is multifaceted, impacting various aspects of a horse’s health, performance, and overall well-being. Here are the key areas where horse weight plays a crucial role:
1. Health Monitoring
- Early Detection of Health Issues: Regular weight monitoring can help identify potential health problems early. Sudden weight loss or gain can indicate issues such as dental problems, metabolic disorders, gastrointestinal diseases, or other underlying conditions.
- Nutritional Balance: Maintaining an appropriate weight ensures the horse receives a balanced diet. Both underweight and overweight horses are at risk of developing health issues related to poor nutrition.
2. Feeding and Nutrition
- Diet Management: Accurate weight measurement helps formulate a diet that meets the horse’s needs. Overfeeding can lead to obesity, while underfeeding can cause malnutrition and related health problems.
- Supplement and Feed Allocation help determine the correct amount of feed, forage, and supplements required to maintain optimal health and performance.
3. Medication and Treatment
- Correct Dosage: The correct dosage of medications, dewormers, and supplements is often based on the horse’s weight. Incorrect dosing can lead to ineffective treatment or adverse effects.
- Preventive Healthcare: Weight management is crucial in preventing conditions such as colic, laminitis, and metabolic syndrome, which are influenced by diet and weight.
4. Performance and Fitness
- Athletic Performance: For performance horses, maintaining an optimal weight is critical for achieving peak performance. Excess weight can reduce speed and endurance, while being underweight can lead to a lack of strength and stamina.
- Conditioning and Training: Weight monitoring helps adjust training programs to ensure the horse builds muscle and maintains fitness without gaining excessive fat.
5. Breeding and Reproduction
- Healthy Reproduction: For breeding horses, maintaining an appropriate weight is essential for reproductive health. Underweight mares may have difficulty conceiving and carrying foals to term, while overweight mares can have complications during pregnancy and foaling.
- Foal Development: Proper weight management of pregnant mares ensures healthy foal development.
6. Safety and Welfare
- Load Bearing: Knowing the horse’s weight is essential for determining its appropriate load, whether for riding or work. Overloading a horse can cause stress, injury, and long-term health issues.
- Transport: Accurate weight measurement is crucial for safe transportation. Overloading transport vehicles can lead to accidents and injuries.
7. Economic and Management Decisions
- Insurance and Valuation: Weight is often a factor in insuring horses and can affect their market value. Accurate weight records are essential for these purposes.
- Resource Allocation: This helps manage resources effectively, such as feed and healthcare, ensuring that each horse’s needs are met without waste.
8. Rescue and Rehabilitation
- Recovery Programs: In rescue and rehabilitation scenarios, monitoring weight is critical for assessing the progress of malnourished or neglected horses and ensuring they return to a healthy state.
Maintaining accurate and regular weight records is a vital aspect of horse management, contributing significantly to their health, performance, and quality of life.
Methods of Calculating Horse Weight
Determining the weight of a horse can be accomplished through several methods, each varying in accuracy and practicality. Here are the primary methods used:
- Weighbridge/Scale
- Description: The most accurate method involves using a large animal scale designed to accommodate the size and weight of horses.
- Process: The horse is led onto the scale, and its weight is directly measured.
- Advantages: Highly accurate.
- Disadvantages: Scales can be expensive and are only sometimes readily available.
- Weight Tape
- Description: A specialized tape measure marked with weight estimates based on the horse’s girth.
- Process: To get a reading, the tape is wrapped around the horse’s girth (the circumference of the horse’s body just behind the front legs).
- Advantages: Affordable, easy to use, and portable.
- Disadvantages: Provides only an estimate and can be less accurate for very fit or unusually shaped horses.
- Mathematical Formula
- Description: Uses specific body measurements to estimate weight through a formula.
- Common Formula:
- In Pounds:
- In Kilograms:
- Measurements Needed:
- Heart Girth: The circumference around the horse’s body just behind the front legs.
- Body Length: From the point of the shoulder to the end of the buttock.
- Advantages: It can be accurate and requires only a measuring tape.
- Disadvantages: It requires careful measurement and calculation and has the potential for human error.
- Body Condition Scoring (BCS)
- Description: While not a direct measure of weight, BCS assesses the horse’s fat cover to provide insight into whether the horse is underweight, overweight, or at an optimal weight.
- Process: Visual and tactile assessment of fat deposits on various parts of the horse’s body, scored on a scale (commonly 1 to 9).
- Advantages: Useful for monitoring changes in condition over time.
- Disadvantages: Subjective and doesn’t provide an actual weight measurement.
Comparison of Methods
Summary
- Weighbridge/Scale: Best for precise weight, ideal for facilities with frequent need for exact measurements.
- Weight Tape is practical for routine checks and most general purposes, especially for owners without access to a scale.
- Mathematical Formula: This formula offers a good balance between accuracy and practicality. It is useful for situations requiring more precision than a weight tape but without access to a scale.
- Body Condition Scoring is complementary to weight measurement and helps assess the horse’s overall condition and health.
Choosing the correct method of calculating horse weight depends on the resources available and the specific needs of the horse owner or caretaker. Regular weight monitoring using one or more of these methods is crucial for effective horse management.
Importance of Knowing Horse Weight
Regularly monitoring and maintaining accurate weight records are fundamental to responsible horse management. The benefits span health and nutrition management, medical treatment, performance optimization, breeding, safety, and economic aspects, all contributing to the horse’s overall well-being and quality of life.