ORF in sheep is a common viral disease of small ruminants that can transmit to human beings. The virus is under the family of poxviridae. The virus mainly affects the mouth, oral cavity, lips, muzzle, tongue, and associated organs. The disease is also called contagious ecthyma or sore mouth in sheep. The disease causes severe economic loss in small animal farms.
Causes of ORF in Sheep
The cause of ORF or contagious pustular dermatitis is poxvirus. The virus is a dsDNA virus, and the primary host is sheep, goats, and other small ruminants. The virus has zoonotic importance and can easily transmit to humans. Numerous strains of the virus can cause severe clinical diseases.
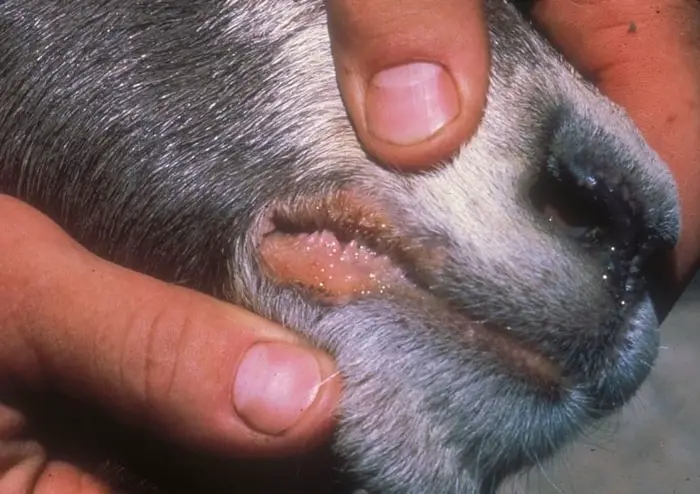
Epidemiology of Contagious Ecthyma in Sheep
The virus is transmitted and spread by direct contact with infected animals like sheep and goats. The infection spreads to lambs, and during suckling, the virus may affect the udder causing mastitis in ewes. The disease is more severe during stress like poor hygiene, overcrowding, stress due to transportation, change of diet, lambing, and environmental conditions.

Clinical Signs of ORF in Sheep
The ORF virus primarily affects the mouth, commissure of lips, muzzle, tongue, gums, and associated tissues. The usual clinical manifestations are:
- Initially, small papules and pustules appear around the mouth.
- The pustules break and cause severe itching.
- Later, the clinical lesions spread to nostrils, eyes, ears, vulva, udder, hooves, and tail. Redness and swelling of the skin of the mouth, muzzle, lips, and nostrils.
- Loss appetite.
- Progressive weakness.
- The infection spread to other organs like the udder, vulva, foot, and hooves.
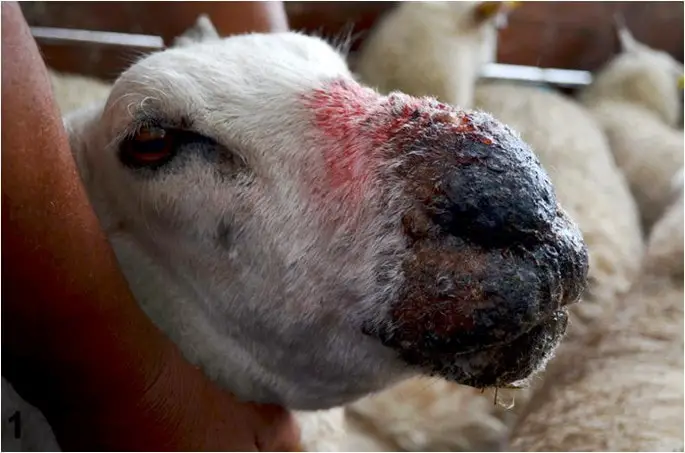
Diagnosis of Contagious Ecthyma in Sheep
The standard procedures of diagnosis of ORF in sheep are:
- History of exposure to infected animals.
- Presence of predisposing factors.
- Specific clinical signs.
- Isolation and identification of causative virus by ELISA, CFT, AGID test.
- PCR of the virus.
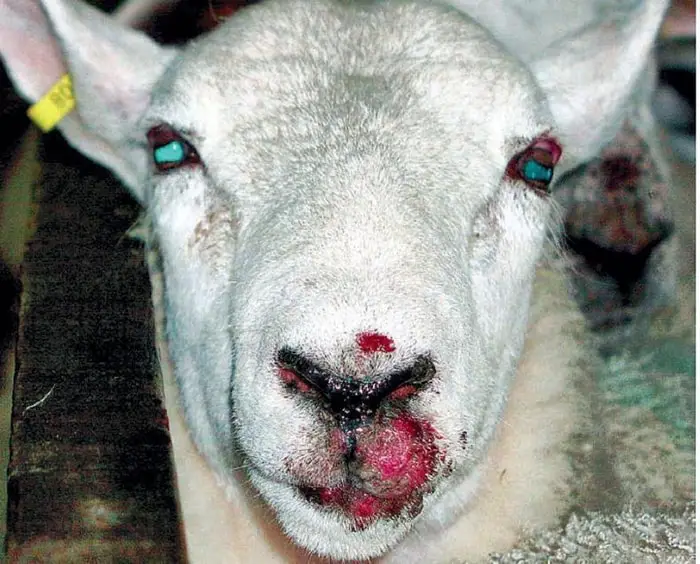
Treatment of ORF in Sheep
There is no specific treatment for a viral disease like ORF or sore mouth in sheep. The treatment will mainly reduce viral load and control secondary bacterial infection. The treatment procedures are:
- Administration of a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
- Antihistamines.
- Wash the mouth and affected organs with 2% boric acid solution.
- Wash the feet, udder, vulva, and sheep house with 0.1% potassium permanganate solution.
Prevention and Control of Contagious Ecthyma in Sheep
Viral disease prevention is more important than treatment. The disease can be prevented by taking the following measures:
- Improve hygiene and sanitation of the sheep house.
- Reduce the stress in the sheep herd.
- Vaccinate against ORF virus or goat pox virus.
- Isolation of affected animals from the healthy herd.
- Daily cleaning of the sheep house.
Concluding Remarks on ORF in Sheep
ORF or contagious ecthyma or sore mouth is a contagious viral disease of sheep, goats, and other ruminant animals. The disease causes severe economic loss of sheep farms by spreading rapidly to the herd, production loss, and treatment cost. The disease can be controlled and spread reduction by taking adequate measures and vaccination.