The term Elbow Dysplasia in dogs means generalized osteoarthrosis of the elbow joint, explicitly including the conditions of the ununited anconeal process (UAP) and fragmented coronoid process (FCP). Therefore, it is crucial when you identify your young dog is limping on a front leg; it may be due to a condition named elbow dysplasia.
It is prevalent in medium to large dog breeds. Symptoms appear your dog breeds are 5-18 months old. Elbow dysplasia in dogs causes pain, swelling, instability, and often leads to arthritis. The disease is often hereditary, and it can be managed with exercise control, physiotherapy, weight control, and pain relief.
Breeds of Dog at Risk of Elbow Dysplasia
Elbow dysplasia is most common in large to medium dogs breed. The breeds at risk of elbow dysplasia are includes-
- Golden Retrievers.
- Labradors.
- German Shepherd.
- Rottweilers.
- Newfoundlands.
- Bassett Hounds.
- Bernese Mountain.
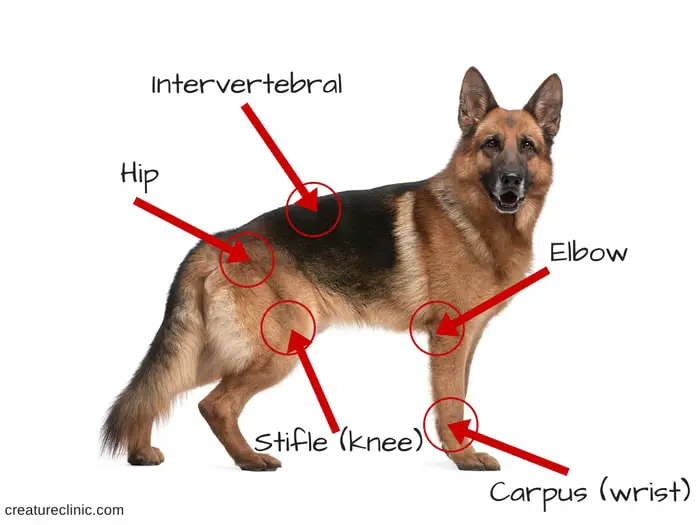
What Causes Dog Elbow Dysplasia?
Because of two diseases, together with osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) of the medial humeral condyle, overlap, the common etiology of osteochondrosis has been proposed. Skeletally immune large and giant breed dogs are affected, and the condition is often bilateral. The cause of UAP and FCP is most often accepted to be unpredictable growth of the radius and ulna. The anconeus develops from a separate ossification center only in large dogs and will generally come to union with the parent ulna by 20 weeks of age. If this union has not occurred by this time, it is considered ununited.
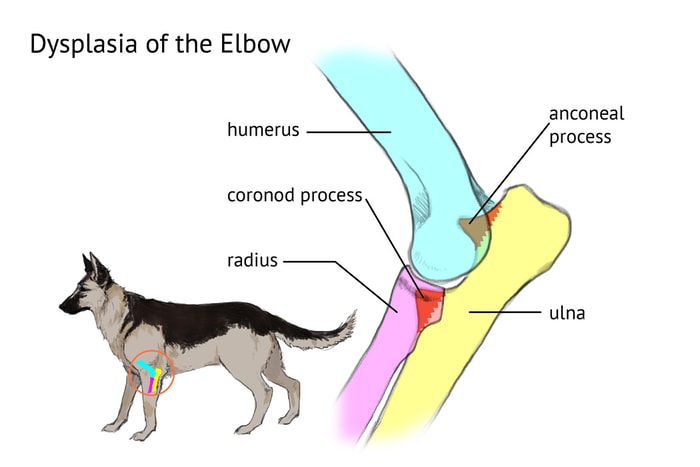
What are the Signs of Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs?
Symptoms often begin when your dogs between 5-18 months old. Both UAP and FCP lead to forelimb lameness with an abnormal gait, joint effusion may be present, and the dog resents elbow manipulation, especially hyperextension and pronation of the antebrachium.
- Stiffness, especially after lying down.
- Reluctance to exercise or to play or go on a walk.
- Often the feet of the front limbs appear turned out.
- Elbow swelling and pain and swollen joints.
- Pain and feel discomfort when extension or flexion of the joint.

Diagnosis of Dysplasia of Dog’s Elbow
Your vet LAP may be diagnosed radiographically by a hyperflexed lateral radiograph of the elbow, revealing the failure of the anconeal process to merge with the proximal ulna in a dog older than five months of age. However, primary lesions associated with a fragmented medial coronoid process are challenging to see radiographically.
The diagnosis of the fragmented medial coronoid process your vet is often made on based upon breed, age, history, clinical signs, and physical examination. Secondary changes such as osteophyte deposition proximal to the anconeal process, caudal to the distal humeral condyle, and anterior to the radial head are radiographic findings consistent with a fragmented medial coronoid process of long-standing. Therefore, the diagnosis of FCP is often of exclusion.
Treatment of Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs
If your dog is at risk of elbow dysplasia, call your vet for advice, and your vet recommended proper feeding and exercise while they are growing.
- The treatment options depend on weight control, pain relief, exercise control, rest, and surgery.
- Treatment for UAP is surgical, either removal or attachment of the process.
- Surgery to include a fragment removal and lesion curettage is the treatment of choice for FCP.

Prognosis of Canine Elbow Dysplasia
Elbow dysplasia is a painful condition in digs that needs lifelong treatment or therapy. The prognosis for both conditions is dependent upon the severity of secondary changes at the time of treatment. Conservative management consists of NSAIDs. SODOAs are also used, often in combination with NSAIDs.