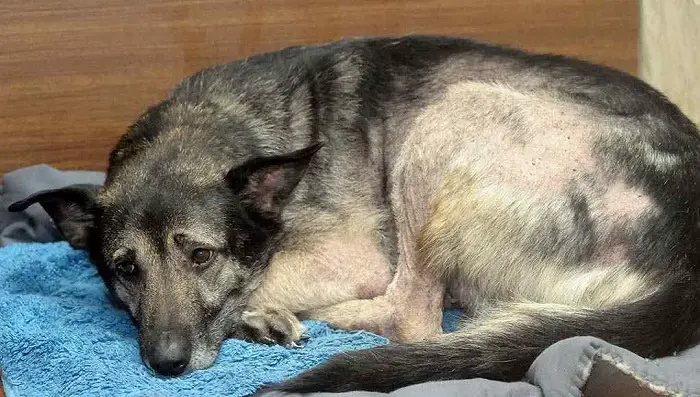
Diarrhea is one of the significant causes of concern in pet animals to visit the veterinarian. Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis, or HGE in dogs, is an acute disease that needs immediate concern. The disease manifests in bloody diarrhea, mucoid feces, dehydration, weakness, and lethargy.
What is HGE in Dogs?
HGE, or hemorrhagic gastroenteritis, is the inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract of dogs. The condition is primarily sudden and shows vomiting, loose feces mixed with blood or mucous, severe dehydration, and weakness. The causal bacteria or organism severely damages the GI tract’s internal layers and causes bleeding.
Causes of Hemorrhagic Gastroenteritis in Dogs
The leading causes of hemorrhagic gastroenteritis are unknown. The probable causes of HGE in dogs are as follows:
- Bacterial infection ( Clostridium perfringens)
- Immune-mediated diseases.
- Toxins.
- Pancreatitis in dogs.
- Intestinal parasites (Ancylostoma caninum).
- Ulcers in the stomach or intestine.
- Foreign bodies in the stomach or intestine.
Risk Factors for HGE in Dogs
The following conditions will enhance the possibility of hemorrhagic gastroenteritis:
- Stress.
- Eat unusual items or sharp objects.
- Trauma.
- Tumor in the stomach.
- Canine Parvovirus infection.
- Coagulation disorders.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Anxiety.
Breeds of Dog Predisposing to Canine HGE
The following dog breeds are more susceptible to HGE in Dogs:
- Miniature Pinscher.
- Yorkshire Terrier.
- Maltase.
- Toy Poddle.
- Miniature Schnauzer.
- Dachshund.
- Cavalier King Charles Spaniel.
- Shetland Sheepdog.
Clinical Signs HGE in Dogs
The disease mostly onset suddenly. The typical clinical signs are as follows:
- Bloody diarrhea.
- Abdominal pain.
- Lack of appetite.
- Lethargy.
- Vomition.
- Pale mucous membrane (gum).
- Dehydration.
- Shock.
- Collapse.
- Hypothermia.
- Occasional fever.
Diagnosis of Canine HGE
The disease can be diagnosed in the following ways:
- History of exposure to sick animals.
- Presence of predisposing causes.
- Typical clinical signs.
- Examination of feces for blood or hemoglobin.
- Culture of feces of affected dog to diagnose causal bacteria.
- Complete blood count.
- Examination of mucous membrane for anemia and dehydration.
- Determination of Packed Cell Volume (PCV) or hematocrit (HCT) value of blood.
- Ultrasonographic examination to determine foreign bodies or tumors in the GI tract.
- Radiographic examination of stomach and intestine.
- You can use rapid tests for the detection of Parvovirus infection.
Treatment of HGE in Dogs
The condition of healthy dogs becomes very critical within a short time if you are left untreated. The line of treatment for hemorrhagic gastroenteritis in dogs is:
- Intravenous fluid therapy to cover immediate fluid loss.
- You can give gastrointestinal protector Sucralfate.
- Anti-vomiting drugs may be given to prevent or stop vomiting.
- You can give a broad-spectrum antibiotic like Ceftriaxone.
- In severe cases, you can give intravenously plasma (fluid portion of blood) or colloidal solution.
- You can give probiotics to contain the gastric environment.
Prevention of Canine Hemorrhagic Enteritis
The success rate of immediate treatment of favorable. The disease can be prevented by maintaining the following measures:
- Feed your dog with high-quality commercial dog food.
- Deworming your dogs every three months at intervals.
- Vaccinate your dogs against potential viral diseases like Parvovirus.
- Maintain a healthy environment for your dog.
- Isolate sick dogs from healthy ones.
- Maintain a low-stress environment for dogs.
- Take special care about the excessive movement of dogs.
Final Advice on HGE in Dogs
Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis is an acute condition caused by various agents and organisms in dogs. The disease manifests as bloody diarrhea, vomiting, anemia, shock, lethargy, and death. Clinical history, signs, and a few diagnostic tests can diagnose the disease quickly. The disease responds very rapidly with favorable treatment. The disease can be prevented by following healthy tips and management.