Toxoplasmosis in cats is a parasitic disease that is caused by the intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii. The disease the most well-known parasitic disease and infects nearly all warm-blooded animals, including pets and humans. It occurs with ocular signs only or with other generalized involvement of the liver, lungs, and meninges. Ocular signs may not be accompanied by systemic signs and are more common in cats than dogs.
Important Information on Toxoplasmosis in Cats
Toxoplasmosis is a widespread and deadly disease of cats. There is significant public health importance of Feline Toxoplasmosis. As a cat owner, you must be cautious about the progress of the disease. In my article, I shall discuss the causes, transmission, clinical findings, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, public health hazards, and clinical manifestations in humans.

Causes of Toxoplasmosis in Cats
Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic disease caused by the obligate intracellular coccidian parasite, Toxoplasma gondii. The organism can infect most animals and birds. Domestic cats and other Felidae are the definitive hosts. All non-feline hosts are intermediate hosts.
Transmission of Feline Toxoplasmosis
Oral ingestion of tissue cysts or oocysts results in the spread of Toxoplasma organisms to extra-intestinal organs via the blood or lymph. The three major transmission modes are congenital infection, ingestion of infected tissues, and ingestion of oocyst contaminated food or water. Other minor ways of transmission include transfusion of fluids or transplantation of organs.

The parasite Toxoplasma gondii is found in garden soil and raw meat. The most common symptoms of toxoplasmosis include loss of appetite, fever, and lethargy. The disease is usually spread by eating poorly cooked food containing exposure to infected cat feces, cysts, and an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy.
The Life Cycle of Toxoplasma Organism
The sporulated oocysts are infectious for most warm-blooded vertebrates and survive in the environment for months to a year. The persistent stage they form in extra-intestinal tissues, particularly CNS, muscles, and visceral organs of immunocompetent individuals. Bradyzoites likely persist in tissues for the life of the host.
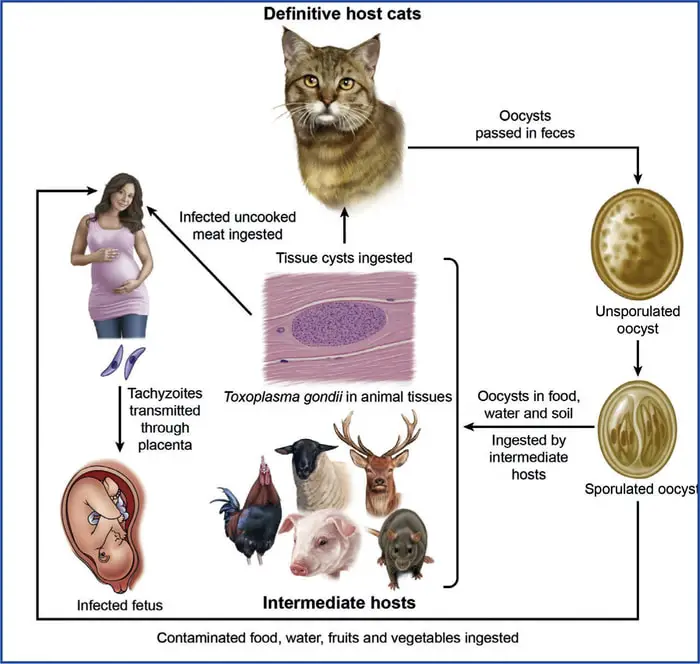
Infection with T. gondii occurs following the ingestion of any of the three life stages or transplacentally when the host has its primary infection during gestation. Ingesting Toxoplasma gondii bradyzoites during carnivorous feeding most commonly infect cats. Because dogs are more coprophagic than cats, the ingestion of sporulated oocysts is a likely means of infection.
Signs and Symptoms of Feline Toxoplasmosis
The most common and recognized clinical signs of toxoplasmosis are as follows:
- Toxoplasmosis is most critical in transplacentally infected kittens. Affected kittens may be stillborn, or affected kittens may have an extended abdomen because of large liver and ascites.
- Encephalitic kittens may be on rest most of the time or cry continuously. The disease may be rapidly deadly in some cats with severe respiratory or CNS signs.
- Fatal extra-intestinal toxoplasmosis can develop from overwhelming intracellular replication of tachyzoites following primary infection of kittens or immune-suppressed adult cats.
- Disseminated toxoplasmosis in cats results in depression, anorexia, fever followed by hypothermia, peritoneal effusion, icterus, dyspnea, and death.
- Chronic syndromes occur in some cats from extra-intestinal infection. The infection can cause anterior or posterior uveitis, fever, muscle hyperesthesia, weight loss, anorexia, seizures, ataxia, icterus, diarrhea, and pancreatitis.

Diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis in Cats
The clinical signs and symptoms make the diagnosis, and the confirmatory diagnosis is based on the following:
- Clinical and laboratory findings.
- Biochemical abnormalities.
- Cytology.
- Radiology.
- Fecal examination for the presence of oocyst in feces.
- Aqueous humor and CSF assessment.
- Organism detection by cell culture.

Treatment of Toxoplasmosis in Cats
When your diagnosis of toxoplasmosis is confirmed, you should have to discuss your experts on whether treatment is necessary. Sulphadiazine and pyrimethamine are two drugs widely used in the treatment of human toxoplasmosis. Pyrimethamine may also be used to supplement clindamycin therapy. Besides, corticosteroids at anti-inflammatory doses can be beneficial adjacent to anti-protozoal therapy.

Appropriate supportive therapy, including physiotherapy, should be given for your cats. Other anti-Toxoplasma drugs include doxycycline, minocycline, azithromycin, and clarithromycin. Your cats with uveitis, you should be treated with anti-Toxoplasma drugs in combination with topical, oral, or parenteral corticosteroids to avoid secondary damage to the eye induced by inflammation.
Toxoplasmosis in Cats Prevention
Preventing toxoplasmosis in cats involve measures intended to reduce the incidence of feline infections and subsequent shedding of oocysts into the environment. Kittens raised outdoors usually become infected just after they are weaned and began to hunt. Your cats should preferably be fed only dry and canned, commercially processed cat food. If meat is given, it should always be well-cooked, even if frozen before feeding.

Public Health Importance of Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic disease and can spread to humans from cats. The public health significance of the disease are as follows:
- Cats found to be spreading T. gondii oocysts should be hospitalized for this period and treated to eliminate shedding, mainly when a pregnant woman is present in the household. To prevent inadvertent environmental contamination, the cat owner should practice proper hygienic measures on a routine basis.
- Children’s sandboxes should be secured to prevent cats from defecating in them. Mechanical vectors such as sowbugs, earthworms, and houseflies, have been shown to contain oocysts, and cockroaches and snails are additional mechanical vectors.
- Sporulated oocysts resist most disinfectants, and only 10% ammonia is useful when it is in contact with contaminated surfaces for 10 minutes. Outbreaks of human infections had reported when oocyst-contaminated dust particles were inhaled or ingested.
Is toxoplasmosis in Cats Contagious to Humans?
When your pets are infected, they can be contagious to humans for three weeks. Toxoplasmosis is transmitted if a human accidentally eats a cat fecal material that contains the toxoplasma organism. The disease is only infectious in feces that are at least 24 hours old.

What are the Symptoms of Human Toxoplasmosis?
The symptoms of Toxoplasmosis in Humans are-
- Fever.
- Shortness of breath and neurological signs that is seizures and lack of coordination.
- Body aches.
- Headache.
- Fatigue.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
How can you Prevent Human Toxoplasmosis?
Prevention of human toxoplasmosis involves avoiding exposure of susceptible hosts, including the unborn fetus and immunosuppressed adult. Risk of exposure by contact with infected meat can be avoided by cooking all meat to an internal temperature greater than 67 degrees C. good personal hygiene dictates that hands be washed well after handling raw meat. Animal care technicians cleaning cat cages should wear masks and protective clothing.
Concluding Remarks on Toxoplasmosis in Cats
Feline toxoplasmosis is a common and severe disease of cats. You can also be affected by the protozoal organism from your cats. So it is a matter of great concern about the health of you, your family members, and the public health importance. The information I have given in the article will help you a lot.