Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis or EPM in horses is a degenerative disease that affects the central nervous system and spinal cord. It is an inflammatory disease of nerve tissues of the brain and spinal cord caused by unicellular protozoa Sarcocystis neurona. More than 50 percent of the horses of the United States are susceptible to the protozoan organism of EPM. Previously the disease was known as segmental myelitis later in 1974 it was identified as a protozoan disease and in 1990 named Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis. There are another protozoan species that also cause EPM in horses is Neospora hughesi but the incidence is less than S neurona.
How Horse get EPM?
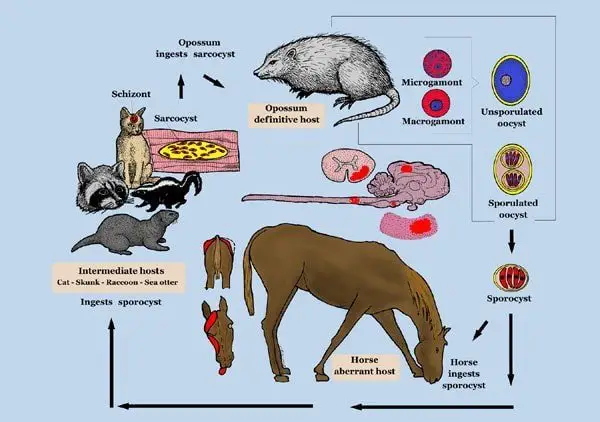
The disease is widely distributed throughout the USA and the actual incidence rate of EPM in horses is difficult to estimate. The parasite has a complex two-host host life cycle: definitive host is opossum and intermediate host are raccoons, skunks, cats, armadillos, and sea otters. The horse is considered as the dead-end of the S neurona as the organism does not spread further. Horses get infected by the ingestion of feed and water contaminated by the feces of the opossum. Horse to horse transmission of the disease does not occur.
What are the Symptoms of EPM in Horses?
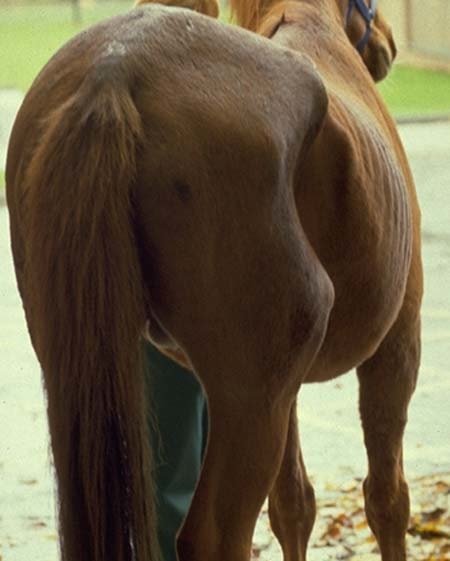
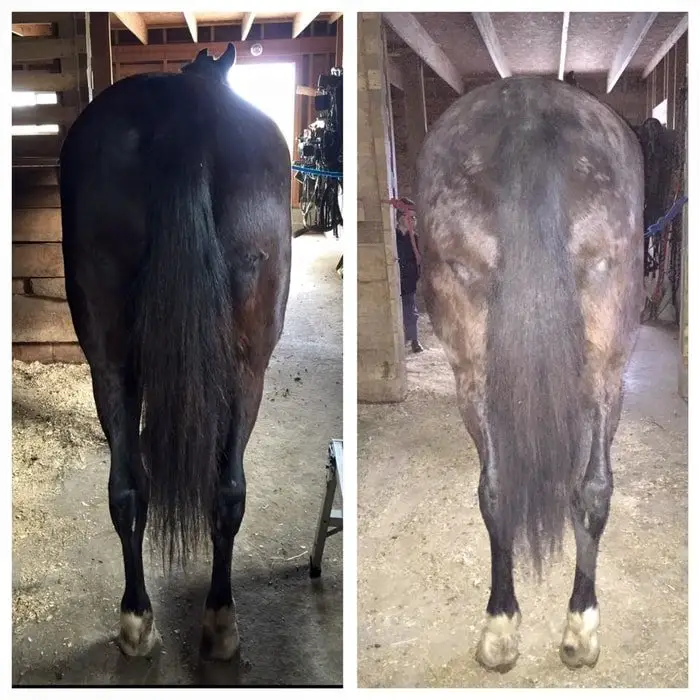
The disease expressed various neurological signs as the organism mainly affects CNS and spinal cords. Clinical signs are varied, asymmetrical and depend on the location of lesions on the brain and spinal cord. The most common symptoms are as follows:
- Incoordination in Movement.
- Spasticity or Stilted movement.
- Abnormal Gait or Lameness
- Muscular atrophy.
- Weakness or incoordination while climbing or going down.
- Muscular paralysis of mouth, eyes, eyelids, and ears.
- Difficulty in swallowing.
- Sweating abnormality.
- Lack of sensation in mouth, face or head region.
- Head imbalance or tilt the head with walls.
- Collapse or seizures.
Diagnostic Methods of Equine Protozoal Encephalomyelitis
The diagnosis of EPM in horses is mainly by clinical signs and symptoms. The same clinical signs may appear in other diseases. Only the expert veterinarian can identify the disease observing other clinical signs like debility, ataxia, muscle incoordination, and paralysis. Definitive diagnosis can be done by serological tests and detection of EPM antibodies in Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF). Prompt and early diagnosis of the disease will help accurate treatment.

What is the Treatment for EPM in Horses?
The prompt treatment of EPM will increase the chance of recovery of your horse. According to the latest FDA approved treatment of EPM are
- Marquis (ponazuril) a product of Merial, which is the paste-like formulation and given once daily for 28 days.
- Antiprotozoal PROTAZIL a product of Merck Animal Health, given with feed for 28 days.
- ReBalance ( Sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine), a product of PRN Pharmaceuticals, liquid suspension given for 90 to 270 days. This drug is very safe and usually given in an empty stomach for better absorption.
- Suppurative treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids.
- Vitamin E is usually given for treating neurological diseases.
Prevention and Control Measures of EPM in Horses
Prevention is better than cure for every infectious disease. The preventive measures of EPM are as follows:
- Reduce grazing
- Control rodents in stable areas.
- Discourage the visit by an opossum in your horse.
- Keep your horse’s feed in a closed container.
- Improve the storage facilities of horse feed.
- Properly dispose of the dead animals to reduce the load contamination.
- Provide clean and safe water for your horse.
- Reduce the scope of water contamination.
- Improve the health check-up by your vet regularly.
Final Advice on Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis
EPM in horses is not a very serious disease but without treatment may lead to progressive death. Moreover, treatment is a costly affair for every disease. The preventive measures for the disease I have discussed are also important for other diseases. As a horse owner, you must keep your horse safe and free from all possible risk factors.
