Dogs and cats have lived together with human wings for thousands of years. Both man and animals mutually benefit by living as close companions. There is a possible transmission of diseases among them. Zoonotic diseases in dogs are those diseases that transmit to human beings from companion animals.
What are Zoonotic Diseases in Dogs
Zoonoses can be defined as those infections that are naturally transmitted between vertebrate animals and men. It is also important to remember that the susceptibilities of humans, dogs, cats, and infectious agents do not necessarily mean that transmission occurs between them.
Most Common Zoonotic Diseases in Dogs
Zoonotic diseases are commonly asymptomatic and harmless in most cases. Few diseases are very harmful and require immediate treatment. Rabies is one of the most emerging zoonotic diseases that need special care and treatment. The other critical zoonotic diseases are Tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, leptospirosis, and leishmaniasis.

1. Rabies in Dogs
Rabies is the most widespread and critical zoonotic disease in the world. The disease is caused by the Rabies virus and spread by direct contact with an infected animal. Wild animals like foxes, raccoons, bats, street dogs, and unvaccinated pet animals are the primary threat to human beings transmitting the disease.
2. Canine Distemper
Canine distemper is the primary cause of disease in dogs. CDV abnormally develops in humans and causes multiple sclerosis.
3. Zoonotic Diseases in Dogs: Canine Calicivirus
Canine Calicivirus infection has been reported in dogs and people associated with diarrhea.
4. Canine Lymphchoriomemingitis
Lyphochorioenisgitis virus is found in wild rodents and rarely transmitted to man. Experimental infection in dogs; dogs to dogs transmission has occurred, but no epidemiological significance has been found. Dogs can also e experimentally infected with human strains of rotavirus, and natural human-canine reassortants have been reported.
5. Reovirus in Dogs
Reoviruses are well known for being able to cross species, but it is unknown whether canine reoviruses are transmitted to humans. The human reovirus infection is generally asymptomatic.
6. Zoonotic Diseases in Dogs: Enteroviruses
Enteroviruses are some coxsackie viruses, and polioviruses can naturally infect dogs. The infected dogs with enteroviruses are unlikely sources of infection to humans.
Bacterial Diseases
7. Cats Scratch Disease
Cat Scratch Disease (CSD) is caused by Bartonella henselae, a gram-negative bacterium. The bacteria is carried by cats and is usually associated with cat-inflicted trauma, like a scratch or bite. B henselae infection in cats produces prolonged and often intense bacteremia, but most animals develop few clinical signs. Clinical Cat Scratch disease in humans is typically characterized by swollen, painful lymph nodes, low-grade fever, muscle aches, and general malaise are common. The disease is mild and self-limiting in more than 90% of cases.
8. Bite Wound
Bite wound is the most frequent and most important canine zoonotic disease. Pasteurella multocida and P pneumomozotropica are found in the mouth of dogs and cats, and P multocida infection is involved in more than 30% of bite infections.
Capnocytophagia canimorsus and C cynodegmi are also part of the normal oral flora of many animal species except men. The organisms are transmitted to humans through bite infections and scratches. In men, they are generally of low pathogenicity, although the infection can kill in the immunosuppressed. Eikcnella corrodents bacteria are generally found in the gingival plaque of dogs and are commonly isolated from dog bites. Pseudomonas, Actinobaculli, Streptococci, Staphylococci, Corynebacteria, and a variety of anaerobes are also frequently isolated from bite wounds.
9. Escherichia Coli Infection
Pathogenic species of E Coli are generally host-specific but can carry transferable genes encoding virulence or antibiotic resistance. E Coli is both enterotoxigenic and enterohaemorrhagic in dogs, but no cases have been found to transfer to humans and vice versa.
10. Zoonotic Diseases in Dogs: Salmonellosis
Salmonella typhimurium is the most frequent zoonotic bacteria, but other species are also seen. Dogs are the primary source of infection in human beings. The prevalence of S Typhimurium is 1-5% of dogs, as a European survey, and up to 50% in the United States of America.
11. Campylobacteriosis in Dogs
Campylobacteriosis in dogs is a bacterial disease caused by Campylobacter jejune. The disease manifests through watery diarrhea, fever, stomach pain, and sometimes bloody stool. The disease is usually asymptomatic but, in young puppies, becomes a severe illness. The symptoms become disappear within 3-5 days without treatment. The bacteria can transmit to human beings from affected dogs.
You must clean your hands with soap after touching affected dogs. Clean the feces and utensils of the affected dog to reduce contamination.
12. Zoonotic Diseases in Dogs: Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is one of the most devastating zoonotic bacterial diseases in dogs. The disease is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The TB organism can affect any organ or system of dogs, and the severity of the disease depends on the organ affected. The most common clinical signs are coughing, weight loss, lack of appetite, loss of condition, and death. The bacteria can spread from affected dogs to humans through contact with cough or sputum.
13. Leptospirosis in Dogs
Leptospirosis is one of the most common bacterial diseases in dogs and other domestic animals. Leptospirosis in dogs is caused by Leptospira canicola. The disease has potential zoonotic importance transmitted to humans from affected dogs. The primary mode of transmission is contaminated water.
14. Rickettsia in Dogs
Rickettsiosis is an important zoonotic disease in dogs caused by Rickettsia rickettsiae. The clinical manifestations and severity of the disease vary from species to species. The most common clinical signs are fever, anemia, coughing, loss of condition, weakness, and lethargy. Bite wounds and blood-sucking of ticks transmit the organism.
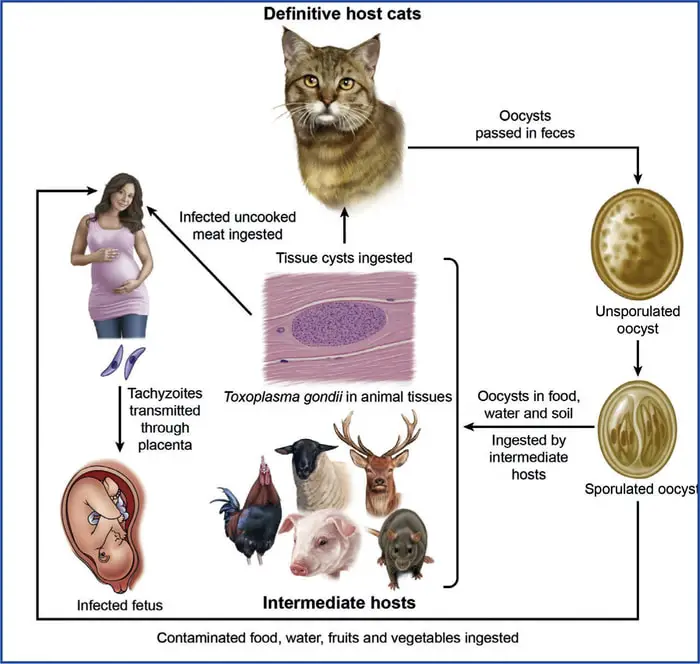
15. Toxoplasmosis in Dogs
Toxoplasmosis is one of the most common protozoan diseases in dogs and cats. The disease is caused by Toxocara canis and T catis. The disease is identified by mucoid diarrhea, weakness, lethargy, loss of fluid, and death due to hypovolemic shock. The organism transmits to humans by direct contact with contaminated feces. The four significant signs in men are fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, and muscle aches.
16. Giardiasis in Dogs
Giardiasis is a significant unicellular protozoal disease in dogs, cats, and humans. The disease is caused by Giardia dudenalis (also called G intetinalis or G lamblia). The disease is seen by diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, abdominal gas formation, and discomfort. The infection of Giardiasis in humans from animals is low and specific.
You may get an infection y ingestion of contaminated food and water from infected animals’ feces. You must clean the poops and dirty utensils of infected dogs and cats. You must clean your hands and face after cleaning the pets. Keep the kids away from diseased pets.
17. Cryptosporidiosis in Dogs
Cryptosporidiosis is a protozoan disease caused by Cryptosporidium canis, C felis, C parvum, and C hominis. The disease is seen in dogs, cats, men, and many other domestic and pet animals. The disease is caused by a water-borne parasite and causes severe diarrhea and fever. The organism affects the intestinal mucosa, reduces nutrition absorption, and causes death due to dehydration.
18. Leishmaniasis in Dogs
Leishmaniasis is a worldwide critical zoonotic disease caused by blood protozoa Leishmania infantum. The organism is transmitted by biting of sand fly. The disease is found in Asia, Europe, Africa, and North and South America. So far, more than 89 countries of the world have found Leishmaniasis. The organism causes both cutaneous and visceral lesions. The disease is seen by diarrhea, anorexia, decreased stamina, weakness, and nose bleeding.
19. Internal Parasitic Diseases
Some internal parasitic diseases, such as Toxocariasis, Echinococcus granulosus infection, and Tania solium, spread from dogs and cats to humans.
20. Zoonotic External Parasitic Diseases
A few external parasitic diseases are ordinarily present in dog and cat skin. The standard external zoonotic parasites are fleas, ear mites, and sarcoptic mange. You must take necessary preventive measures to control those parasites.
The Final Talk on Zoonotic Diseases in Dogs
Dogs and cats live with a close companions, especially with kids. Many zoonotic diseases in dogs easily transmit to a human companion. In my article, I have mentioned the most common zoonotic diseases for your safety. The preventive measures that I have highlighted, please follow accordingly. You and your family, including lovely pets, will have a better life.